MxNi100−x (M = Ag, and Co) nanoparticles supported on CeO2 nanorods derived from Ce–metal organic frameworks as an effective catalyst for reduction of organic pollutants: Langmuir–Hinshelwood kinetics and mechanism†
Abstract
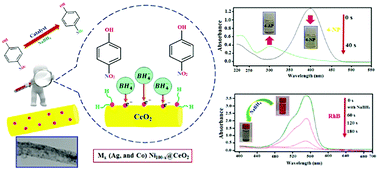
In this study, AgxNi100−x, and CoxNi100−x (x = 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100) bimetallic nanoparticles were successfully decorated on the surface of CeO2 nanorods derived from Ce–metal organic frameworks (Ce–MOF). The as-synthesized products were characterized using different techniques including XRD, FE-SEM, EDX, TEM, ICP, and BET. The as-prepared nanocomposites showed remarkable catalytic activity towards the reduction of organic pollutants such as 4-nitrophenol (4-NP), and rhodamine-B dye (RhB) by NaBH4 solution, with high stability and reusability for five consecutive cycles. The obtained results indicated that among these nanocomposites, Ag80Ni20@CeO2, and Co60Ni40@CeO2 exhibited the best catalytic performance, with high turn over frequency. The adsorption equilibrium constants of borohydride (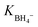 ), and 4-nitrophenol (K4-NP) were determined by the Langmuir–Hinshelwood model, and the reaction mechanism was investigated in detail. The thermodynamic parameters including energy of activation, activation enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy were calculated, and discussed.
), and 4-nitrophenol (K4-NP) were determined by the Langmuir–Hinshelwood model, and the reaction mechanism was investigated in detail. The thermodynamic parameters including energy of activation, activation enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy were calculated, and discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...