Microstructure regulation of microencapsulated bio-based n-dodecanol as phase change materials via in situ polymerization
Abstract
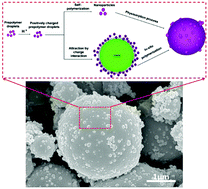
Phase change materials (PCMs) are considered as a promising alternative in the field of thermal energy storage and heat transfer because of their high energy density. Microencapsulated PCMs, i.e. the PCMs enclosed in micron-sized shells, have been studied extensively as a route to avoid PCM leakage and facilitate their applications. In this study, a series of microencapsulated bio-based n-dodecanol with various surface morphologies were synthesized through in situ polymerization. The microencapsulation mechanism and microstructure evolution under varying factors such as precursor concentration, emulsifying condition and resin ratio were investigated via ex situ field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). In particular, the surface morphology, particle size and dispersion of microcapsules were analyzed systematically. The self-polymerized nanoparticles located on the surface of the microcapsules could be regulated, and their formation mechanism was also determined. In addition, the regulation parameters of microencapsulation could also be beneficial for the further rational design of microcapsules, and are expected to expand their application to wider fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...