Flux improvement, rejection, surface energy and antibacterial properties of synthesized TiO2-Mo.HNTs/PVC nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes†
Abstract
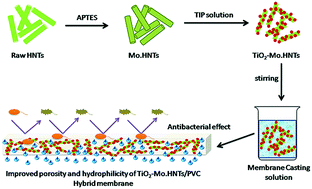
The present work demonstrates the preparation of modified halloysite loaded with titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles and its use as a nanofiller in a poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) hybrid ultrafiltration (UF) membrane for advanced water treatment. Modification of raw halloysite nanotubes (rHNTs) with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) was performed, after which TiO2 nanoparticles were synthesized using titanium(IV) isopropoxide (TIP) solution on the surface of the modified HNTs (Mo.HNTs) using the sol–gel method. Novel hybrid UF membranes (TiO2-Mo.HNTs/PVC) were prepared by blending of TiO2-Mo.HNTs nanofiller in different concentrations using a classical phase inversion method. Pure water flux of the hybrid UF membrane (197.5 ± 3.6 L m−2 h−1 in 2 wt% hybrid UF membrane) improved consistently with an increasing amount of nanofiller in the membrane matrix. The hydrophilicity of the membrane samples increased (contact angle as low as 68.8° ± 5.6° in 3 wt% hybrid UF membrane) and interfacial surface free energy was also high (−ΔGSL 98.22 mJ m−2 in 3 wt% membrane), as compared to the membrane without nanofiller. The rejection of BSA and HA by all TiO2-Mo.HNTs/PVC (1–3 wt%) membranes was greater than 80%. TiO2-Mo.HNTs played an important role in stopping pollutants during membrane filtration; and antibacterial activity of the TiO2-Mo.HNTs/PVC hybrid UF membranes against E. coli was high (95–97.5% in 2 wt% and 3 wt% hybrid membrane). Thus TiO2-Mo.HNTs played an important role in the separation processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...