Alismanoid A, an unprecedented 1,2-seco bisabolene from Alisma orientale, and its protective activity against H2O2-induced damage in SH-SY5Y cells†
Abstract
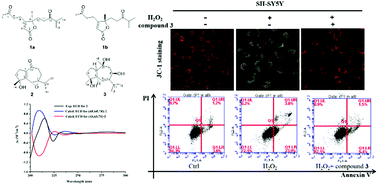
A pair of novel sesquiterpenoids, (8R)-alismanoid A (1a) and (8S)-alismanoid A (1b), possessing an unprecedented 1,2-seco bisabolene carbon skeleton, were isolated from rhizomes of Alisma orientale together with two new sesquiterpenoids: a 15-nor guaiane alismanoid B (2) and alismanoid C (3). Their structures were elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR, HRESIMS, electronic circular dichroism (ECD), and theoretical calculations, and a plausible biosynthetic pathway for compound 1 is discussed. Meanwhile, compounds 1–3 were investigated for their protective effects on H2O2-induced damage in human dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y), and compounds 1b, 2, and 3 showed significantly protective activities at a certain concentration. Further, the action mechanism of compound 3 was proved to be through inhibition of H2O2-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Herein, these results suggest that sesquiterpenoids are potential candidate drugs for treating Parkinson's disease induced by reactive oxygen species.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...