Synthesis of strontium hexaferrite nanoplates and the enhancement of their electrochemical performance by Zn2+ doping for high-rate and long-life lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
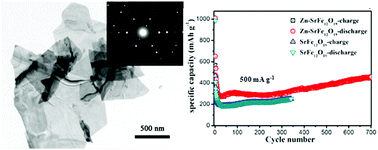
Hexagonal structured strontium hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) nanoplates with diameters of ca. 0.6–2.5 μm and thicknesses of 40–60 nm have been successfully synthesized by adjusting the Fe/Sr ratios via a solvothermal process followed by annealing. Zn2+-Doped strontium hexaferrite nanoplates were fabricated as above, except that zinc was also added. The as-prepared Zn2+-doped SrFe12O19 and SrFe12O19 nanoplates were then evaluated as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) for the first time. The electrochemical measurements showed that both the Zn2+-doped SrFe12O19 and SrFe12O19 nanoplates had high reversible capacities of 1015.8 mA h g−1 and 456.5 mA h g−1, respectively, after 270 cycles at a current density of 100 mA g−1. In addition, both samples exhibited good high-rate cycling performances; in particular, the Zn2+-doped SrFe12O19 nanoplates delivered 457.6 mA h g−1 at a high current density of 500 mA g−1 after 700 cycles. Therefore, strontium hexaferrites could be investigated as a candidate for long-life lithium-ion batteries. The superior cycling performances exhibited by Zn2+-doped SrFe12O19 are ascribed to the zinc-doping, which can efficiently enhance the electronic conductivity and improve the lithium ion diffusion of SrFe12O19; this was confirmed by impedance measurements.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...