Selective trace determination of lead ions in different agricultural products using a novel core–shell magnetic ion-imprinted polymer with the aid of experimental design methodology†
Abstract
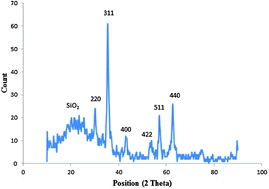
One of the most toxic and hazardous elements affecting human health is lead, which is known to be a carcinogenic factor, causing harmful effects on human metabolism. Our study deals with the preparation of a novel and selective magnetic ion-imprinted polymer (Fe3O4@SiO2@IIP) with the application of isatin as a ligand and 4-vinylpyridine (4-VP) as a functional monomer for the selective and efficient extraction of Pb(II) ions from various fruits and vegetable samples. A Box–Behnken design was applied with several variables for optimization of the extraction and elution steps. In the selected conditions, the detection limit, preconcentration factor, and sorption capacity of this new polymer were 0.13 ng mL−1, 324.3, and 83 mg g−1, respectively. Finally, the feasibility of Fe3O4@SiO2@IIP nanoparticles was evaluated by extraction and determination of Pb(II) ions in different fruits and vegetables such as apples, kiwis, carrots, cantaloupes, peaches, cucumbers, and tomatoes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...