Stability and durability studies of TiO2 coated immobilized system for the degradation of imidacloprid†
Abstract
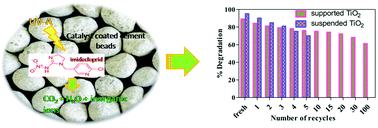
The present article demonstrates the use of supported TiO2 for studying the degradation of an insecticide, imidacloprid (IMI), along with durability studies of the catalyst. Operating conditions for the best degradation were optimized in suspension mode by varying the dose of TiO2, H2O2, pH and area/volume ratio of the batch reactor. With all conditions optimized, approximately 95% degradation of IMI was achieved after 3 h of photocatalytic treatment. For fixed-bed studies, TiO2 coated spherical cement beads were used for the degradation of IMI. Studies on the number of catalyst coatings, calcination temperature and catalyst durability were undertaken for the degradation. Spherical beads having a diameter of around 2.0 cm with two coatings of catalyst were efficient enough for 89% degradation of IMI after 6 h of treatment. The stability and efficacy of the supported catalyst were assessed by recycling the beads more than 30 times. The catalyst was characterized by SEM/EDS, XRD and DRS analysis. The durability of the catalyst was further confirmed by using catalyst coated beads that had previously been used for 100 cycles. The mineralization of IMI was validated by reduction in COD along with chloride ion (Cl−1) generation. A tentative degradation pathway for IMI has been proposed by carefully identifying the intermediates using GC-MS analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...