Analysis of the degradation mechanism of the polyarylene ether anion-exchange membrane for alkaline fuel cell and water-splitting cell applications†
Abstract
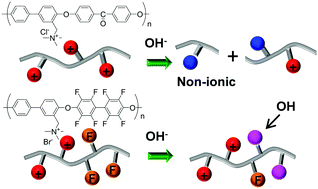
Model compounds of benzyltrimethylammonium (BTMA)-modified polyethersulfone, polyetheretherketone, and polyetheroctafluorobiphenyl were synthesized to analyze the degradation mechanism in alkaline fuel cell and water-splitting cell applications. From the degradation behavior of the model compounds, it was found that the BTMA-modified polyethersulfone and polyetheretherketone membranes were decomposed via ether cleavage-triggered simultaneous degradation of the backbone and the anion-exchange group. In contrast, polyetheroctafluorobiphenyl anion-exchange membranes were deteriorated by the direct nucleophilic substitution of fluorine groups in the main chain by hydroxide groups. To enhance the alkaline stability of polyarylene ether anion-exchange membranes, it is critical to not introduce electron-withdrawing groups and increase electron density around the ether linkages. The degradation rate of the model compounds was considerably accelerated in alkoxide solution compared with aqueous solution, indicating that the alkaline stability of the membrane was significantly more important in methanol or ethanol fuel cells than in hydrogen fuel cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...