Preparation and temperature-dependent photoluminescence properties of ScF3:Eu3+ submicroparticles†
Abstract
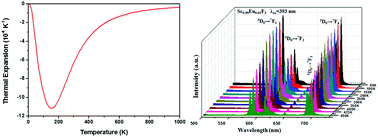
In this study, negative thermal expansion (NTE) ScF3 submicroparticles were prepared and selected as host material. Various Eu3+ concentrations (0.05–50%) in the doped ScF3 particles were obtained and their temperature-dependent photoluminescence (PL) properties were studied. The phase confirmation and morphology of the as-prepared ScF3 particles were investigated by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The XRD results reveal that when the doping concentration reaches 3%, the EuF3 phase begins to form. The size of the ScF3 cubic particles ranges from 300 nm to 800 nm. The ScF3:Eu3+(1%) submicroparticles were prepared and their PL properties were evaluated. The temperature-dependent luminescence results reveal that the luminescence intensity increases with the decrease in temperature in the range from 80 K to 450 K. Moreover, the decay time increases with a decrease in temperature. The crystal structure, electronic properties, dielectric functions, and absorption spectra have been systematically investigated for the Eu3+-doped ScF3. First principles calculations were used to support and explain our experimental observations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...