Chemically modified biopolymer as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a neutral chloride environment†
Abstract
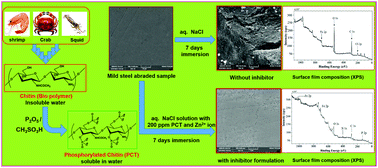
The present study is aimed at the development of a novel, eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor based on a naturally occurring biopolymer. Chitin or poly(N-acetyl-1,4-β-D-glucopyranosamine) is one of the most abundant naturally occurring polysaccharides. It is a biological polymer, which is known to be non-toxic, biocompatible, and enzymatically biodegradable. In the present study, chitin has been chemically modified to phosphorylated chitin (P-chitin or PCT) in order to increase its solubility in aqueous medium and its ability of complexation with metal ions. The inhibition effect of PCT and PCT in combination with low concentrations of Zn2+ on the corrosion of mild steel in an aqueous environment containing 200 ppm NaCl has been studied using weight-loss, potentiodynamic polarization, and electrochemical impedance techniques. The synergistic effect of this functionalized biopolymer and Zn2+ is established from the results. This synergistic formulation afforded an inhibition efficiency of 94% for mild steel in a low chloride environment. The protective film formed on the mild steel surface has been investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The mechanistic aspects of corrosion inhibition are discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...