Tunable near-infrared fluorescent gold nanoclusters: temperature sensor and targeted bioimaging†
Abstract
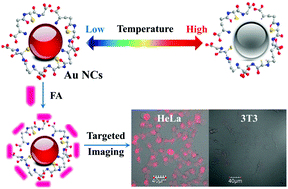
Near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence nanomaterials with low toxicity and long wavelength emission play an important role in bioapplications. Herein, a simple and rapid microwave heating method is designed to synthesize fluorescent gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) by using glutathione (GSH) as a reducing agent and stabilizing agent simultaneously. By adjusting the microwave heating time, the as-prepared GSH–AuNCs can show size-dependent tunable fluorescence from the visible region to the NIR region, and even to 800 nm wavelength. Besides, the as-prepared GSH–AuNCs are water-soluble, low toxicity and highly stable, and exhibit multifunctional surface chemistry based on GSH as the protective surface layer. Another attractive feature of the resultant NIR GSH–AuNCs is temperature-dependent fluorescence and they could be used as a nanoprobe to measure the temperature in the range from 0 to 80 °C. Moreover, this process is reversible, which means that the fluorescence intensity of the GSH–AuNCs can be recovered to the initial intensity when the temperature changes reversibly. Finally, the resultant NIR GSH–AuNCs are further conjugated with folic acids (FAs) which helps the AuNCs target HeLa cells. These properties provide FA-conjugated GSH–AuNCs with potential applications as a platform for cancer diagnosis studies in various biological systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...