On the complexation of metal cations with “pure” diethylenetriamine-N,N,N′,N′′,N′′-pentakis(methylenephosphonic) acid†
Abstract
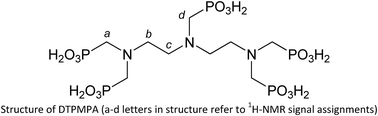
The complex formation between a series of biologically, environmentally, and technologically relevant cations (namely Sn2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+ and Al3+) and diethylenetriamine-N,N,N′,N′′,N′′-pentakis(methylenephosphonic) acid (DTPMPA) has been investigated in NaCl aqueous solutions at I = 0.1 and 0.3 mol dm−3 and T = 298.15 K. The ligand used has been obtained in sufficient purity by a new efficient synthetic procedure for the determination of accurate and reliable data on its acid–base properties and metal complex formation. The stability constants determined in this work under different experimental conditions have been then used to assess the speciation of many systems containing the above-cited cations, and to quantify the sequestering ability of DTPMPA toward them, by means of the calculation of several pL0.5 values under various conditions simulating those of many real systems where this chelant is employed as a cationic sequestrant. Finally, some 1H- and 31P-NMR studies have also been performed to gain a further insight into the binding mode of DTPMPA toward metal cations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...