Understanding the speciation of Ln(iii) complexes with octadentate tripodal ligands†
Abstract
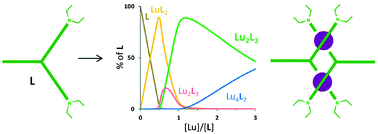
Two new dissymmetrical tripodal ligands bearing three multidentate pyridine moieties (L5 and L6) have been synthesised and the speciation of their Ln(III) complexes in solution has been studied. The complexation behaviour with selected Ln(III) has been investigated by combining ESMS, spectrophotometric and NMR titrations. For both ligands LX (X = 5, 6), the Ln2(LX)3 species are abundantly present at stoichiometry in the form of unconventional low-symmetrical complexes. However, the complexes with L5 at [Ln]/[L5] ∼1 are much better defined and allow the corresponding 1H-NMR spectrum to be completely assigned. Indeed, the latter points out that the structure of complexes [Ln2(L5)2]6+ in solution is best described as an unsaturated dinuclear helicate, where the tridentate sites are wrapped about the metallic cations, and the bidentate strand does not coordinate. Compared to L4 and L6, the prolongation of the spacer in L5 (glycine moiety) has in fact allowed thermodynamic and kinetic stabilities to increase, especially for the Lu(III) complexes. Finally, the structure of dinuclear species [Ln2(LX)2]6+ (X = 4–6) is apparently independent of the structure of the bidentate moieties, which are involved in complexation in metal excess only.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...