A gold nanocluster-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for cysteine and homocysteine detection in living cells†
Abstract
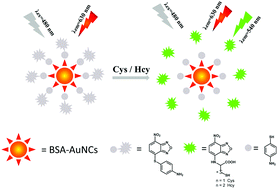
A novel organic–inorganic ratiometric fluorescent probe AuNCs–NBD was developed for the detection of cysteine (Cys) and homocysteine (Hcy). In our design, the AuNCs–NBD exhibited dual-emission fluorescence properties with a single excitation. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) protected gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) with carboxyl groups were employed as a reference signal unit and conjugated with the p-aminothiophenol substituted NBD (7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole) moiety to form the ratiometric fluorescent probe. The AuNCs–NBD composite showed a single red fluorescence at 630 nm ascribed to AuNCs, and reaction of AuNCs–NBD with Cys and Hcy caused the cleavage of the thioether bond and therefore generated the fluorescent amino linked NBD with emission at 540 nm. Accordingly, the green fluorescence of released NBD at 540 nm gradually increased upon increasing the concentration of Cys or Hcy, while the red fluorescence ascribed to AuNCs at 630 nm remained constant, which resulted in the ratiometric determination of Cys and Hcy using the AuNCs–NBD probe. Due to the specific recognition of NBD with Cys and Hcy, the AuNCs–NBD probe exhibited high selectivity for Cys and Hcy over other amino acids and GSH. In addition, the AuNCs–NBD composite displayed desirable properties such as high specificity, appreciable solubility, ratiometric fluorescence response and favorable detection limit. Moreover, the AuNCs–NBD probe has been successfully applied for monitoring and imaging of intracellular Cys and Hcy in HeLa cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...