Microwave treated sol–gel synthesis and characterization of hybrid ZnS–RGO composites for efficient photodegradation of dyes
Abstract
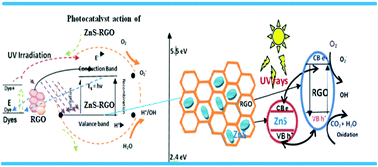
In the present work, assembly of nanosized ZnS particles grown on the surface of a 2D platform of reduced graphene oxide (RGO) sheets by the sol–gel method without the use of any surfactant/stabilizing agents and treatment with a microwave irradiation technique was reported. During this process, the RGO sheets act as the substrate, matrix and fine template for the growth/decoration of isometric ZnS nanoparticles and graphene sheets were formed simultaneously. The synthesized nanocomposites were used as photocatalyst materials for the degradation of Brilliant Blue and Brilliant Yellow dyes under UV light radiation. The results signify that the nanocomposites exhibit an enhanced photocatalytic activity compared to PZnS and RGO, owing to the high specific surface area, and the reduction of photoinduced electron–hole pair recombination in ZnS, which are due to the inclusion of RGO and its synergetic effects. Reduced graphene oxide acts as an excellent electron transporting material and effectively suppresses the charge recombination of ZnS–RGO nanocomposites exhibiting much higher photoresponse activity. The chemical composition, morphology and microstructural features of the materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction, FTIR, UV-Vis spectroscopy, photoluminescence, Raman and energy dispersive spectroscopy, FE-SEM, XPS, and TEM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...