Catalytic assembly of DNA nanostructures on a nanoporous gold array as 3D architectures for label-free telomerase activity sensing†
Abstract
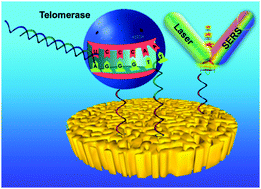
Telomerase, an enzyme known to catalyze telomere elongation by adding TTAGGG [thymine (T), adenine (A), and guanine (G)] repeats to the end of telomeres, is vital for cell proliferation. Overexpression of telomerase has been found in most tumor cells, resulting in telomere dysfunction and uncontrolled cellular proliferation. Thus, telomerase has been considered as a potential cancer biomarker, as well as a potential target in cancer therapy. In this study, telomerase-catalyzed growth of tandem G-quadruplex (G4) assembled on a nanoporous gold array (NPGA) resulted in the formation of three-dimensional hybrid nanoarchitectures. The generated nanostructure then captured malachite green (MG) (reporter molecule) without the need of a complicated labeling process. Upon laser irradiation, the captured MG molecules produced a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) signal that was generated by an abundant amount of plasmonic hot spots in the NPGA substrates. A limit of detection (LOD) of 10−10 IU along with a linear range, which was 3 orders of magnitude, was achieved, which was equivalent to the telomerase amount extracted from 20 HeLa cells. The LOD is 2 orders of magnitude better than that of the commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and it approaches that of the most sensitive technique, telomeric repeat amplification protocols (TRAP), which require a laborious and equipment-intensive polymerase chain reaction (PCR). In addition, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was used to chemically identify and quantify the telomerase activity on the sensitized NPGA surface. Furthermore, the sensor was applied to screen the effectiveness of anti-telomerase drugs such as zidovudine, thus demonstrating the potential use of the sensor in telomerase-based diagnosis and drug development. Moreover, the framework represents a novel paradigm of collaborative plasmonic intensification and catalytic multiplication (c-PI/CM) for label-free biosensing.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Horizons Community Board Collection: Biosensors


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...