Development of highly active anti-Pneumocystis bisbenzamidines: insight into the influence of selected substituents on the in vitro activity†
Abstract
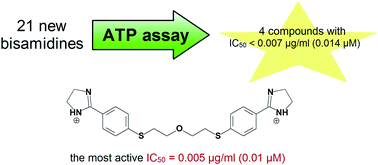
Here we describe the potency of 21 pentamidine analogues against the fungal pathogen, Pneumocystis carinii, in an ATP bioluminescent assay with toxicity profiles in 2 mammalian cell lines. Reduction of two 5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole rings was applied to the synthesis of acid-labile bisamidines. Anti-Pneumocystis activity is discussed in the context of 3 groups of compounds depending on the main structural changes of the pentamidine lead structure. The groups include: 1) 1,4-bis(methylene)piperazine derivatives 1–5; 2) alkanediamide derivatives 6–10; 3) alkane-derived bisbenzamidines 11–21. IC50 values of 18 compounds were lower than the IC50 of pentamidine. Four bisamidines were active at nanogram concentrations. Introduction of sulfur atoms in the alkane bridge, replacement of the amidino groups with imidazoline rings, or attachment of nitro or amino groups to the benzene rings is responsible for remarkable activity of the new leading structures. The vast majority of compounds, including four highly active ones, can be classified as mild or nontoxic to host cells. These compounds show promise as candidates for new anti-Pneumocystis agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...