Antiproliferative activities of alkaloid-like compounds†
Abstract
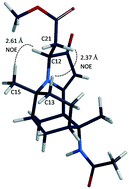
Tricyclic alkaloid-like compounds were synthesised in a few steps, via the bridging Ritter reaction. The compounds were evaluated for their antiproliferative activity against the MCF-7 and the aggressive MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. The anti-cancer activities of 2c were found to be selective towards the aggressive and more challenging to treat triple negative (MDA-MB-231) cell line while exhibiting no antiproliferative activities towards the MCF-7 cells at the highest concentration tested (50 μM). The IC50 of compound 2c was determined to be 7.9 μM for the MDA-MB-231 cell line. Furthermore, 2c arrested cell cycle at the G2/M phase and induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. Besides in-house anti-cancer screening, compound 3 was selected for anti-cancer screening by the National Cancer Institute and was found to have broad anti-cancer activity with selectivity against particular leukaemia, colon, melanoma, and breast cancer cell lines. Cytotoxicities of compounds 2c and 3 were also tested against noncancerous mammalian cells (VERO cell line), and found to be selective towards cancerous cells. The facile synthetic route, unique chemical structures and the biological data make these alkaloid-like compounds worthwhile lead compounds for further anti-cancer drug development.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...