New application of tiplaxtinin as an effective FtsZ-targeting chemotype for an antimicrobial study†‡
Abstract
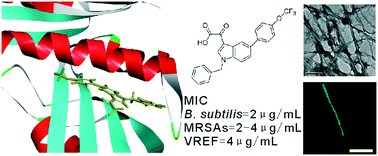
The filamenting temperature-sensitive mutant Z (FtsZ) protein is generally recognized as a promising antimicrobial drug target. In the present study, a small organic molecule (tiplaxtinin) was identified for the first time as an excellent cell division inhibitor by using a cell-based screening approach from a library with 250 compounds. Tiplaxtinin possesses potent antibacterial activity against Gram-positive pathogens. Both in vitro and in vivo results reveal that the compound is able to disrupt dynamic assembly of FtsZ and Z-ring formation effectively through the mechanism of stimulating FtsZ polymerization and impairing GTPase activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...