Synergic modulation of the inflammatory state of macrophages utilizing anti-oxidant and phosphatidylserine-containing polymer–lipid hybrid nanoparticles†
Abstract
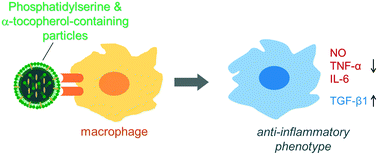
Inflammatory activation of macrophages is a key factor in chronic inflammatory diseases such as ulcerative colitis. The excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS)/reactive nitrogen species (RNS) by macrophages causes oxidative stress during the inflammatory response and exaggerates inflammatory lesions in ulcerative colitis. Inhibition of the inflammatory activation of macrophages is a promising treatment for chronic inflammatory diseases. Here, we prepared self-filling polymer–lipid hybrid nanoparticles (PST-PLNPs) consisting of poly DL-lactic acid as a hydrophobic biodegradable polymer core encapsulating α-tocopherol (T) and phosphatidylserine (PS) both on the surface and interior of the particle. We confirmed the anti-inflammatory response of these hybrid nanoparticles in activated murine macrophages. PS has anti-inflammatory effects on macrophages by modulating the macrophage phenotype, while α-tocopherol is an antioxidant that neutralizes ROS. We found that PS-containing (PS-PLNPs) and PS plus α-tocopherol-containing (PST-PLNPs) polymer–lipid hybrid nanoparticles significantly increased the viability of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated macrophages compared with phosphatidylcholine-containing PLNPs. PST-PLNPs had a better effect than PS-PLNPs, which was attributed to the synergy between PS and α-tocopherol. This synergic action of PST-PLNPs reduced NO and pro-inflammatory cytokine (IL-6) production and increased anti-inflammatory cytokine (TGF-β1) production when incubated with activated macrophages. Thus, these self-filling biodegradable polymer–lipid hybrid nanoparticles (PST-PLNPs) containing anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory molecules might be potential alternative drug carriers to liposomes and polymeric nanoparticles for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases such as ulcerative colitis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...