Discovery of potential antifungal triazoles: design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and preliminary antifungal mechanism exploration†‡
Abstract
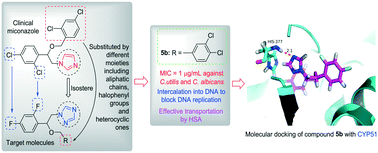
A series of triazoles as miconazole analogues was designed, synthesized and characterized by IR, NMR, MS and HRMS. All the newly prepared compounds were screened for their antifungal activities against five kinds of fungi. The bioactive assay showed that most of the synthesized compounds exhibited good or even stronger antifungal activities in comparison with the reference drugs miconazole and fluconazole. In particular, the 3,4-dichlorobenzyl derivative 5b showed a comparable or superior activity against all the tested fungal strains to standard drugs, and formed a supramolecular complex with CYP51 via the hydrogen bond between the 4-nitrogen of the triazole nucleus and the histidine residue. Preliminary experiments revealed that both of the active molecules 5b and 9c could intercalate into calf thymus DNAs, which might block DNA replication to exhibit their powerful antifungal abilities. Further studies indicated that compound 5b might be stored and transported by human serum albumin through hydrophobic interactions, specific electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonds. These results strongly suggested that compound 5b could serve as a promising antifungal candidate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...