Advances in indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 medicinal chemistry
Abstract
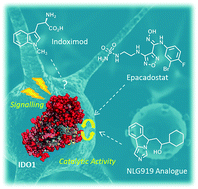
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) mediates multiple immunoregulatory processes including the induction of regulatory T cell differentiation and activation, suppression of T cell immune responses and inhibition of dendritic cell function, which impair immune recognition of cancer cells and promote tumor growth. On this basis, this enzyme is widely recognized as a valuable drug target for the development of immunotherapeutic small molecules in oncology. Although medicinal chemistry has made a substantial contribution to the discovery of numerous chemical classes of potent IDO1 inhibitors in the past 20 years, only very few compounds have progressed in clinical trials. In this review, we provide an overview of the current understanding of structure–function relationships of the enzyme, and discuss structure–activity relationships of selected classes of inhibitors that have shaped the hitherto few successes of IDO1 medicinal chemistry. An outlook opinion is also given on trends in the design of next generation inhibitors of the enzyme.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...