Effects of guanidino modified aminoglycosides on mammalian membranes studied using a quartz crystal microbalance†‡
Abstract
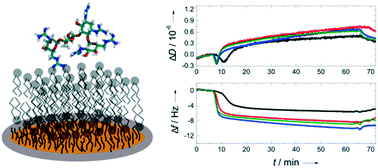
The increase in bacterial and viral resistance to current therapeutics has led to intensive research for new antibacterial and antiviral agents. Among these, aminoglycosides and their guanidino derivatives are potent candidates targeting specific RNA sequences. It is necessary that these substances can pass across mammalian membranes in order to reach their intracellular targets. This study investigated the effects of the aminoglycosides kanamycin A and neomycin B and their guanidino derivatives on mammalian mimetic membranes using a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D). Lipid bilayers as membrane models were deposited onto gold coated quartz crystals and aminoglycosides added afterwards. Notably, the guanidino derivatives exhibited an initial stiffening of the membrane layer indicating a quick insertion of the planar guanidino groups into the membrane. The guanidino derivatives also reached their maximum binding to the membrane at lower concentrations than the native compounds. Therefore, these modified aminoglycosides are promising agents for the development of new antimicrobial treatments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...