3D proteochemometrics: using three-dimensional information of proteins and ligands to address aspects of the selectivity of serine proteases†‡
Abstract
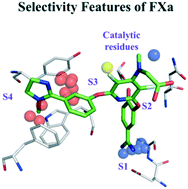
The high similarity between certain sub-pockets of serine proteases may lead to low selectivity of protease inhibitors. Therefore the application of proteochemometrics (PCM), which quantifies the relationship between protein/ligand descriptors and affinity for multiple ligands and targets simultaneously, is useful to understand and improve the selectivity profiles of potential inhibitors. In this study, protein field-based PCM that uses knowledge-based and WaterMap derived fields to describe proteins in combination with 2D (RDKit and MOE fingerprints) and 3D (4 point pharmacophoric fingerprints and GRIND) ligand descriptors was used to model the bioactivities of 24 homologous serine proteases and 5863 inhibitors in an integrated fashion. Of the multiple field-based PCM models generated based on different ligand descriptors, RDKit fingerprints showed the best performance in terms of external prediction with Rtest2 of 0.72 and RMSEP of 0.81. Further, visual interpretation of the models highlights sub-pocket specific regions that influence affinity and selectivity of serine protease inhibitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...