A novel method for identifying potential disease-related miRNAs via a disease–miRNA–target heterogeneous network†
Abstract
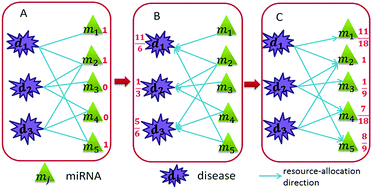
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), as a kind of important small endogenous single-stranded non-coding RNA, play critical roles in a large number of human diseases. However, the currently known experimental verifications of the disease–miRNA associations are still rare and experimental identification is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Accordingly, identifying potential disease-related miRNAs to help people understand the pathogenesis of complex diseases has become a hot topic. In this study, we take advantage of known disease–miRNA associations combined with a large number of experimentally validated miRNA–target associations, and further develop a novel disease–miRNA–target heterogeneous network for identifying disease-related miRNAs. The leave-one-out cross validation experiment and several statistical measures demonstrate that our method can effectively identify potential disease-related miRNAs. Furthermore, the good predictive performance of 15 common diseases and the manually confirmed analyses of the top 30 candidates of hepatocellular carcinoma, ovarian neoplasms and breast neoplasms further provide convincing evidence of the practical ability of our method. The source code implemented by our method is freely available at: https://github.com/USTC-HIlab/DMTHNDM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...