Lipidomic alterations of in vitro macrophage infection by L. infantum and L. amazonensis†
Abstract
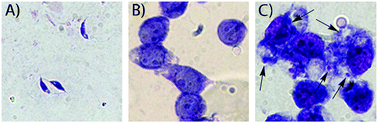
Particular lipid profiles have been found in two different protozoa of the Leishmania genus. Leishmania infantum, a visceral leishmaniasis causative agent and Leishmania amazonensis, a cutaneous leishmaniasis, reveal distinctive lipid contents of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine plasmalogens, sphingolipids, phosphatidylinositols, phosphatidylcholine, and phosphatidylethanolamine, which have been shown to be related to species, life-cycle of the parasite, and macrophage infection. L. infantum displayed a higher content of phosphatidylethanolamine plasmalogens than L. amazonensis, which may help to differentiate their unique clinical manifestations. Phosphatidylserines plasmalogens are also found to be an important lipid class for the intracellular form of the parasite. Our findings also reveal lipid classes that may be involved in visceralization pathways and parasite differentiation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...