Aggregation behavior of novel heptamethine cyanine dyes upon their binding to native and fibrillar lysozyme†
Abstract
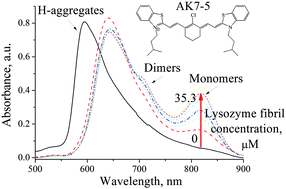
Two newly synthesized symmetrical heptamethine cyanine dyes, AK7-5 and AK7-6, absorbing in the region of low autofluorescence of biological samples, have been tested for their ability to detect proteins aggregated into amyloid fibrils. In aqueous solution these probes possess three absorption bands corresponding to the monomer, dimer and H-aggregate species. The association of the dye with fibrillar lysozyme was followed by the enhancement of the monomer band and the reduction of the H-band. The absorption spectra measured at various fibril concentrations were analyzed in terms of the model allowing for the shift of equilibria between various dye species due to the binding of monomers and dimers of AK7-5 and AK7-6 to amyloid fibrils. The association constants and stoichiometries of the dye–fibril complexation have been evaluated. In contrast to fibrillar lysozyme, the native protein brought about strong J-aggregate formation accompanied by a marked drop in the absorbance of the dye monomer species. Quantum chemical calculations and simple docking studies showed that AK7-5 and AK7-6 monomers can bind to the grooves, running parallel to the fibril axis. Due to their ability to distinguish between the native and fibrillar protein states, the novel cyanines are recommended as complementary to existing amyloid markers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...