Identifying the common genetic networks of ADR (adverse drug reaction) clusters and developing an ADR classification model†
Abstract
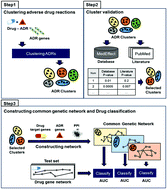
Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are one of the major concerns threatening public health and have resulted in failures in drug development. Thus, predicting ADRs and discovering the mechanisms underlying ADRs have become important tasks in pharmacovigilance. Identification of potential ADRs by computational approaches in the early stages would be advantageous in drug development. Here we propose a computational method that elucidates the action mechanisms of ADRs and predicts potential ADRs by utilizing ADR genes, drug features, and protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks. If some ADRs share similar features, there is a high possibility that they may appear together in a drug and share analogous mechanisms. Proceeding from this assumption, we clustered ADRs according to interactions of ADR genes in the PPI networks and the frequency of co-occurrence of ADRs in drugs. ADR clusters were verified based on a side effect database and literature data regarding whether ADRs have relevance to other ADRs in the same cluster. Gene networks shared by ADRs in each cluster were constructed by cumulating the shortest paths between drug target genes and ADR genes in the PPI network. We developed a classification model to predict potential ADRs using these gene networks shared by ADRs and calculated cross-validation AUC (area under the curve) values for each ADR cluster. In addition, in order to demonstrate correlations between gene networks shared by ADRs and ADRs in a cluster, we applied the Wilcoxon rank sum statistical test to the literature data and results of a Google query search. We attained statistically meaningful p-values (<0.05) for every ADR cluster. The results suggest that our approach provides insights into discovering the action mechanisms of ADRs and is a novel attempt to predict ADRs in a biological aspect.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...