A metabolomic study on high-risk stroke patients determines low levels of serum lysine metabolites: a retrospective cohort study†
Abstract
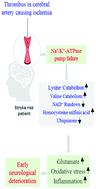
Identifying changes in serum metabolites during cerebral ischemia is an important approach for early diagnosis of thrombotic stroke. Herein, we highlight novel biomarkers for early diagnosis of patients at high risk of thrombotic stroke using high resolution metabolomics (HRM). In this retrospective cohort study, serum samples obtained from patients at risk of thrombotic stroke (n = 62) and non-risk individuals (n = 348) were tested using HRM, coupled with LC-MS/MS, to discriminate between metabolic profiles of control and stroke risk patients. Multivariate analysis and orthogonal partial least square-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) were performed to determine the top 5% metabolites within 95% group identities, followed by filtering with p-value <0.05 and annotating significant metabolites using a Metlin database. Mapping identified features from Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and Mummichog resulted in 341 significant features based on OPLS-DA with p-value <0.05. Among these 341 features, nine discriminated the thrombotic stroke risk group from the control group: low levels of N6-acetyl-L-lysine, 5-aminopentanoate, cadaverine, 2-oxoglutarate, nicotinamide, L-valine, S-(2-methylpropionyl)-dihydrolipoamide-E and ubiquinone, and elevated levels of homocysteine sulfinic acid. Further analysis showed that these metabolite biomarkers are specifically related to stroke occurrence, and unrelated to other factors such as diabetes or smoking. Lower levels of lysine catabolites in thrombotic stroke risk patients, as compared to the control, supports targeting these compounds as novel biomarkers for early and non-invasive detection of a thrombotic stroke.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...