Experimental verification of simultaneous desalting and molecular preconcentration by ion concentration polarization†
Abstract
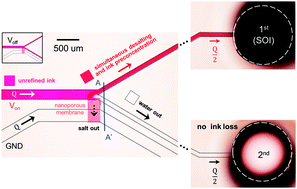
While the ion concentration polarization (ICP) phenomenon has been intensively researched for the last decade, a complete picture of ion and analyte distributions near nanoporous membranes is strongly desired, not only for fundamental nano-electrokinetic studies but also for the development of lab-on-a-chip applications. Since direct concentration measurements, using either time-consuming collection or microelectrodes, are limited due to low throughput (<nL min−1 in typical micro/nanofluidic device) and Faradaic reactions, respectively, we measured the concentration changes of prefilled solutions in individual reservoirs in this work. As a result, analytes larger than the size of nanopores were completely repelled by the ICP layer, 65% of cations were transported through the nanoporous membrane to sustain the ICP phenomenon, and the remaining anions were consumed by electrode reactions for electro-neutrality requirements. These combined effects would enable the perfect recovery of a target analyte and the removal of unnecessary salts simultaneously. Using this scenario, the novel concept of an ink recycler was also demonstrated in this work. We showed that 40% of unnecessary salt, which causes serious deterioration of inkjet heads, was removed, while the concentration of ink molecules was doubled in a single-step operation. This simultaneous desalting and molecular preconcentration mechanism would be a key operational strategy of various refinery/purification applications for drug discovery and the chemical industry, etc.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...