Ultrasensitive detection of trace amounts of lead in water by LIBS-LIF using a wood-slice substrate as a water absorber
Abstract
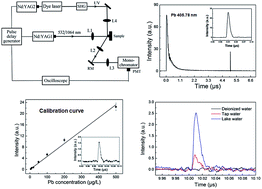
To realize ultrasensitive detection of trace amounts of lead in water, laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with laser-induced fluorescence (LIBS-LIF) was investigated. A wood-slice substrate was selected: (i) as a water absorber to convert liquid-sample analysis to solid-sample analysis; (ii) to eliminate the influence of a water matrix to spectral analysis (e.g., light blocking due to water splashing and plasma emission quenching due OH groups) in the plasma during direct analysis of water samples. The wood slice after treatment was ablated by a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser to produce plasma. Then, the lead atoms in the plasma were re-excited by a second tunable dye laser resonantly. The LIF signal of lead was detected to improve its sensitivity to spectral analysis significantly. Under the assistance of this matrix-converting method, the calibration curve of lead in water samples was created and the limit of detection was found to be 0.32 ppb, two orders of magnitude better than that obtained by analyzing water samples directly using the same LIBS-LIF technique. This sample-pretreatment procedure was rapid and easy to handle. Upon combination with LIBS-LIF, ultrasensitive detection of trace amounts of toxic metal elements in water could be realized. This approach could be applied in water-quality control and monitoring of environmental pollution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...