Co embedded within biomass-derived mesoporous N-doped carbon as an acid-resistant and chemoselective catalyst for transfer hydrodeoxygenation of biomass with formic acid†
Abstract
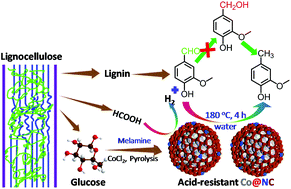
An N-doped Co@C catalyst (Co@NC) is synthesized by a one-pot carbonization of biomass-derived glucose and harmless melamine with CoCl2 as the catalyst, where C and N resources could be transformed into highly graphitic N-doped carbon, while the coordinated Co2+ ions are reduced to uniform Co nanoparticles (NPs), which are embedded in N-doped graphitic structures. Under base-free conditions with formic acid (FA) as a hydrogen donor, the optimized Co@NC-700 (pyrolyzed at 700 °C) shows a highly efficient H2 generation from FA and the best activity for vanillin hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) with FA. For example, Co@NC-700 exhibits 15.4 times higher activity in comparison with uncovered Co on AC (Co/AC), and affords >95% vanillin conversion with 2-methoxy-4-methylphenol (MMP) as the sole product at 180 °C for 4 h. Compared with molecular hydrogen, Co@NC-700 gives a much higher activity and MMP selectivity for vanillin HDO with FA. The Co@NC-700 demonstrates enhanced acid resistance in acidic medium and adsorption of vanillin, and is recyclable and versatile for hydrogenating various unsaturated compounds. The superior performance of Co@NC-700 could be ascribed to N-derived defective sites on Co@NC, which could play multiple roles as base additives in FA dehydrogenation and as a metal-like active center in vanillin HDO.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...