Immobilized bifunctional phosphonium salts as recyclable organocatalysts in the cycloaddition of CO2 and epoxides†
Abstract
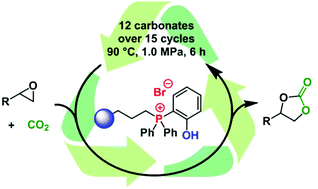
Several bifunctional phosphonium salt catalysts were prepared and immobilized on silica and polystyrene supports. The immobilized systems were compared with their homogeneous analogs in cyclic carbonate synthesis. Interestingly, in some cases, higher activities were observed for the immobilized catalysts. The most active system was a phenol-functionalized phosphonium salt supported on a silica surface. The covalent linkage of the phosphonium unit to the silica was verified by solid-state NMR and FT-IR. SEM and EDX measurements revealed a homogeneous distribution of the phosphonium salt on the particle surface. This catalyst facilitated the addition of CO2 to epoxides under mild conditions. The evaluation of the substrate scope and the catalyst recycling were combined in one set of experiments. In 15 consecutive runs, the synthesis of 12 cyclic carbonates in yields of up to 98% was achieved. The investigation of the catalyst after the recycling experiments revealed the loss of the original anion (bromide) as well as a decrease in the number of phosphonium units, which explained the observed deactivation of the catalyst during the recycling experiments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...