Quantitative N-glycoproteomics of milk fat globule membrane in human colostrum and mature milk reveals changes in protein glycosylation during lactation†
Abstract
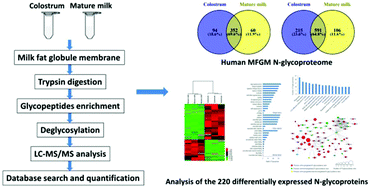
Milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) proteins have recently gained increasing attention, due to their significant biological function. However, the glycosylation of proteins in human MFGM during lactation has not been studied in detail. In this study, through mass spectroscopy-based N-glycoproteomics, we analyzed protein glycosylation of human MFGM. A total of 912 N-glycosylation sites on 506 N-glycoproteins were identified in human colostrum and mature milk MFGM. Among them, 220 N-glycoproteins with 304 N-glycosylation sites were differentially expressed in colostrum and mature milk MFGM. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis revealed various biological processes, cellular components, and molecular functions of the differentially expressed N-glycoproteins. Specifically, these glycoproteins were involved in biological processes such as single-organism processes, biological regulation, regulation of biological processes, response to stimulus and localization; were cellular components in organelles, membranes, and the extracellular region; and had different molecular functions such as protein binding, receptor activity, and hydrolase activity. KEGG pathway analysis suggested that the majority of the differentially expressed N-glycoproteins were associated with phagosome, cell adhesion molecule and some disease-related pathways. Our results provide an in-depth understanding of the quantitative changes in N-glycosylation of proteins in human colostrum and mature MFGM, and extend our knowledge of the N-glycoproteome and of the distribution of N-glycosylation sites in human MFGM during lactation, providing insight into the biological functions of the highlighted glycoproteins.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...