Sulforaphane protects MLE-12 lung epithelial cells against oxidative damage caused by ambient air particulate matter
Abstract
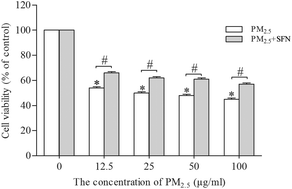
Ambient air particulate matter with aerodynamic diameters ≤2.5 μm (PM2.5) can cause pulmonary injury. Oxidative stress is thought to be an important mechanism of PM2.5-mediated toxicity. Sulforaphane (SFN), a compound derived from cruciferous vegetables, is a well-known potent antioxidant; however, its protective effect on lung epithelial cells exposed to PM2.5 is unclear. The results showed that SFN pre-treatment markedly inhibited PM2.5-induced apoptosis of the type II alveolar epithelial cell line MLE-12 by elevating glutathione S-transferase levels and decreasing reactive oxygen species. SFN pre-treatment down-regulated the expression of the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bad, and reduced the activity of caspase-3, while it up-regulated the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. Moreover, SFN induced the activation of the Akt and ERK pathways, and up-regulated the expression of Nrf2 and its downstream antioxidant genes NQO-1 and HO-1. This is the first study to demonstrate that SFN could protect MLE-12 cells against PM2.5-induced oxidative damage via activation of the Nrf2 pathway and inhibition of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway; therefore, SFN may be a promising compound for preventing PM2.5-triggered pulmonary cell damage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...