Green tea infusion protects against alcoholic liver injury by attenuating inflammation and regulating the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway in C57BL/6 mice†
Abstract
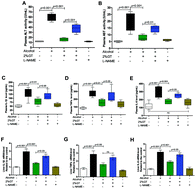
Alcohol intake is a major risk factor for the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver diseases. Accumulating evidence suggests that green tea protects against alcoholic liver injury; however, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. The present study investigated the role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in the protective effects of green tea against alcohol-induced liver injury and inflammation. Ethanol was intragastrically administered to male C57BL/6 mice once a day, and the mice were allowed free access to green tea infusion or water for two weeks. We assessed the plasma levels of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, hepatic contents of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, malondialdehyde and triglyceride and hepatic mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-6). Our results showed that compared with water alone, green tea infusion markedly reduced liver damage, hepatic oxidative stress, hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammatory response. Green tea infusion also significantly reduced hepatic nuclear factor-κB expression and its downstream inflammatory mediators (inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2) mRNA levels in ethanol-treated mice. Additionally, green tea infusion significantly activated hepatic phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and phosphorylated protein kinase B (Akt), which are associated with the upregulation of phosphorylated eNOS expression and the increase of plasma nitric oxide levels in ethanol-treated mice. Furthermore, the protective effects of green tea infusion were considerably inhibited by the eNOS inhibitor NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester in ethanol-treated mice. In conclusion, our study demonstrated that the protective effects of green tea infusion on alcohol-induced liver injury and inflammation involve the modulation of the PI3K/AKT/eNOS pathway.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...