Role of dietary onion in modifying the faecal bile acid content in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet†
Abstract
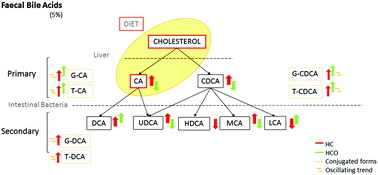
The determination of faecal bile patterns offers new opportunities in the search for non-invasive biomarkers of disease status. The objective of this study was to describe the shifts in faecal bile acid (BA) composition induced by feeding a high-cholesterol/cholic acid diet (HC) over 7 weeks of experimental feeding in Wistar rats, and to evaluate the effect of onion included as a functional ingredient (HCO). A HPLC–MS/MS method allowed the detection of 29 bile acids, 10 of which were tentatively identified and 12 confirmed and quantified by means of standards and calibration curves. The excretion of bile acids revealed a discriminating bile acid profile between the HC and HCO groups compared with the C group. HCO feeding indicated significant changes in specific primary and secondary BA in both the unconjugated and conjugated forms caused by the addition of the onion ingredient to the diet. The results suggest that the induction of microbiome modifications by the HC and HCO diets acts as a critical modifier of the faecal bile acid composition. These modifications might reflect and be linked to changes in the reabsorption of BA at an intestinal level and the process of BA deconjugation in the course of hypercholesterolemia.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...