Sesamin prevents apoptosis and inflammation after experimental myocardial infarction by JNK and NF-κB pathways†
Abstract
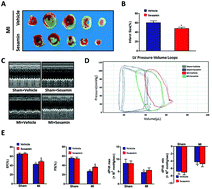
Myocardial infarction is a devastating event, especially when reperfusion is not performed. The inflammatory response has been associated with the pathogenesis of left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. This study focused on the anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of sesamin on ligation of the left anterior descending artery in an experimental mouse model and the potential mechanism underlying the activation of JNK and NF-κB pathways. Mice with MI induced by surgical left anterior descending coronary artery ligation were treated with sesamin by gavage for 1 week. Results showed that after treatment with sesamin, MI-induced cardiac damage was alleviated significantly, indicated by the histopathological examination. The myocardial apoptosis in the border zone was dramatically reduced by sesamin, resulting from the altered expression of apoptosis factors. Moreover, treatment with sesamin also mitigated the inflammatory response, decreased expression of cytokines and the inactivation of NF-κB (nuclear factor κB) signaling. Sesamin decreased the levels of p-JNK protein, which in turn inactivated pro-apoptotic signaling events by restoring the balance between mitochondrial pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 and Bax proteins. Thus, our study suggests that sesamin could alleviate MI-induced cardiac dysfunction through decrease of myocardial apoptosis and inflammatory response.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...