Impact and consequences of polyphenols and fructooligosaccharide interplay on gut microbiota in rats
Abstract
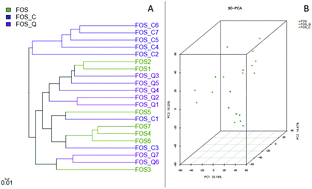
Both fructooligosaccharide (FOS) and polyphenols can be individually and directly transferred to the large intestine of mammals and are beneficial for human health as they reshape the composition of gut microbiota. The combination impact of FOS and polyphenols on rats' gut microbiota and the corresponding consequences on rats were investigated via MiSeq sequencing technique and bioinformatics. The results showed that the combination of different phenolic compounds and FOS displayed distinct impact on the host. The addition of catechin to a FOS diet inhibited Firmicutes and enhanced Bacteroidetes. Moreover, the content of each short chain fatty acid fluctuated in various groups because different unique bacterial species survived or were inhibited under three conditions. On the other aspects, the supplement of catechin controlled the body weight (BW), up-regulated serum leptin, induced more soluble carbohydrates and less soluble polysaccharides in feces, and inhibited or activated some specific genera. The inhibition of genera by catechin could be responsible for the degradation of carbohydrates in gut and the activation of genera might be keystones for the increment of serum leptin. The effect of consuming FOS and/or polyphenols on the health of hosts needs to be further explored.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...