Selective co-production of acetate and methane from wastewater during mesophilic anaerobic fermentation under acidic conditions†
Abstract
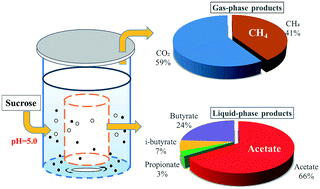
The production of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) from wastewater is considered as another promising way, in addition to methane (CH4) production, to utilize wastewater resources. To simplify or even circumvent the downstream separation and purification steps, selective production of a specific VFA is highly desirable. In this study, we report a continuous, selective co-production of acetate and CH4 during the anaerobic wastewater treatment under mesophilic (35 ± 1 °C) and acidic (5.0) conditions. At a stable stage, acetate accounted for 66% of the liquid-phase products, whereas CH4 accounted for 41% of the gaseous products. A consistent microbial community distribution was observed, where Clostridium, Bacteroides, and hydrogenotrophic methanogens were enriched at pH 5.0, creating a low hydrogen (H2) partial pressure environment to favor the selective acetate production. In contrast, the reactor performance deteriorated at pH 4.0 due to the suppression of microbial activities. This study demonstrates the feasibility of diverting the anaerobic fermentation pathway towards the selective co-production of acetate and CH4via adjusting the wastewater pH and may provide implications for optimizing anaerobic wastewater treatment processes for improved resource recovery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...