Quantitative evaluation and in vivo visualization of mercury ion bioaccumulation in rotifers by novel aggregation-induced emission fluorogen nanoparticles†
Abstract
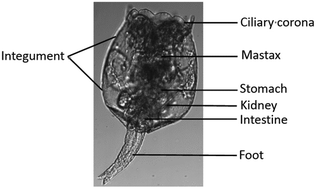
In this study, a specifically-designed aggregation-induced emission fluorogen (AIEgen) with nanoparticle aggregates was used to quantitatively evaluate the bioaccumulation of Hg2+ and visualize Hg2+ kinetics in vivo within the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis for the first time. Quantitative results showed that a sharp drop in Hg2+ concentration occurred at the very beginning in the medium containing rotifers and Hg2+, showing a quick initial uptake of Hg2+ by the rotifers, and then the concentration in the medium plateaued after 5 min. With an increase in rotifer density, the amount of bioaccumulation increased in the rotifer. However, the bioaccumulation efficiency of Hg2+ decreased from 5.28 μg mg−1 h−1 at a low rotifer density of 0.093 mg ml−1 to 2.61 μg mg−1 h−1 at a high rotifer density of 0.375 mg mL−1. Moreover, the fluorescence images and spectra results illustrate that the ingestion of Hg2+ by the rotifer was via its mouth surrounded by the ciliary corona to the digestive tract, and Hg2+ could not permeate into the body integument through diffusion during the study period. Hg2+-induced fluorescence in rotifers dissipated in 6 h after staining, possibly through defecation and excretion. This study indicates that inorganic mercury can be quickly ingested by a rotifer via feeding, but is unlikely deposited as methylated mercury in rotifer tissues.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...