In situ XAS study of CoBi modified hematite photoanodes†
Abstract
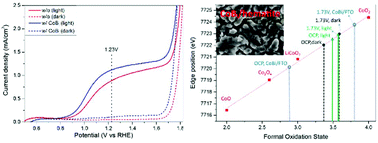
Solar water splitting is a potentially scalable method to store solar energy in the form of renewable hydrogen gas. In this study, we demonstrate that the photoelectrochemical (PEC) performance of hematite photoanodes can be improved by modification with the oxygen evolution catalyst CoBi. The current density at 1.23 V of the pristine hematite under one sun is 0.88 mA cm−2 and it increases to 1.12 mA cm−2 after CoBi modification (∼27% improvement). The presence of a CoBi cocatalayst layer is proposed to improve the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) kinetics and also to prevent electron–hole recombination at the surface via passivating surface defects as well as suppressing the tunneling of electrons from the hematite core, thus improving the photocurrents and resulting in a negative shift of photocurrent onset potentials. These effects of CoBi modification are supported by experimental data obtained by performing electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), PEC and incident photon-to-current efficiency (IPCE) measurements. To investigate the electronic structure of the CoBi cocatalyst deposited on hematite, XPS and in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) are employed. Co K-edge spectra at different potentials and light conditions are recorded. This makes the present work different from most of the previous studies. Using a quantitative analysis method, information on the mean oxidation state of Co in the CoBi film under applied potential and illumination is revealed. We also compare different methods for determining the oxidation state from the edge position and find that the integral method and half height methods are most suitable. In summary, the present work underlines the improvement of the semiconductor/cocatalyst interface of oxygen evolving photoanodes and strengthens the importance of in situ XAS spectroscopy when studying catalysts. This study is the first report so far combining the studies of the PEC performance of a CoBi modified hematite nanorod array photoanode and in situ XAS at the Co K-edge.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...