Switching the electromagnetic properties of multicomponent porous carbon materials derived from bimetallic metal–organic frameworks: effect of composition
Abstract
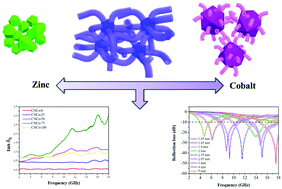
Porous carbon materials have long been regarded as promising candidate for high-performance lightweight microwave absorption materials owing to their strong attenuation abilities, tunable dielectric properties and low density. Nevertheless, previous work mainly focused on binary composites (usually carbon and magnetic fillers), which show limited loss mechanisms. The effect (except temperature) on the interfacial polarization and electromagnetic properties has rarely been investigated. Thus, a series of bimetallic zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (BMZIFs) with designed compositions and highly porous structures were selected to be converted to porous carbon-wrapped semiconductors (ZnO, Co3ZnC) and magnetic metal (Co) composites. Strong dielectric loss capabilities could be provided by graphitic carbon and enhanced interfacial polarization induced by multiple components and unique microstructures. By changing the molar ratio of Zn/Co under a fixed carbonization temperature, the interface of this multicomponent system could be adjusted, which influenced the electromagnetic properties. When evaluated as microwave absorption material, a reflection loss of −32.4 dB could be achieved with a broad effective frequency bandwidth of 5.24 GHz at only 1.9 mm. This work may provide an effective method to modify the physical and chemical properties of porous carbon materials with a desired complex structure and excellent microwave absorption performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...