Diverse reactivity trends of Ni surfaces in Au@Ni core–shell nanoparticles probed by near ambient pressure (NAP) XPS†
Abstract
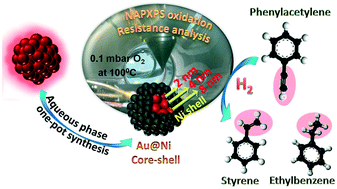
A mild temperature sequential reduction method in aqueous medium is reported for the synthesis of Au@Ni nanoparticles with a core–shell morphology. The nickel shell thickness with a gold core in the nanostructure can be tuned from 2 nm up to about 10 nm. Near ambient pressure XPS (NAPXPS) studies under oxygen atmosphere show that Au80@Ni20 with an extremely thin nickel shell (∼2 nm) follows a distinctly different decomposition pathway of metastable Ni(OOH) species compared to those with larger shell thickness which behave more like individual nickel surfaces. Thus, Ni(OOH) on Au80@Ni20 decomposes to metallic Ni at 100 °C and is found to resist oxidation at 0.1 mbar oxygen at this temperature. Those with a larger nickel shell thickness behave more like monometallic Ni in terms of their decomposition and oxidation properties. The Au@Ni system with an ultra thin metallic nickel overlayer (2 nm) shows high catalytic activity and selectivity for phenylacetylene hydrogenation under mild conditions which outweighs their monometallic counterparts and those with higher nickel shell thickness.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...