Effects of CO2 on the deactivation behaviors of Co/Al2O3 and Co/SiO2 in CO hydrogenation to hydrocarbons†
Abstract
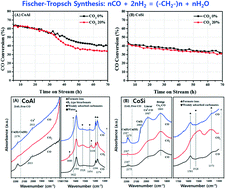
Different deactivation behaviors of the prototype Co/γ-Al2O3 (CoAl) and Co/SiO2 (CoSi) catalysts under an excess CO2 environment were investigated in terms of the surface oxidation and aggregation of cobalt crystallites for the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS) reaction. The presence of excess CO2 in the syngas feed largely altered the catalytic activity and product distribution, especially on the CoAl catalyst. A relatively faster deactivation and lower C5+ selectivity under an excess CO2 environment were observed on CoAl compared with the CoSi, which also were fairly stable under the same reaction conditions. From measurements of the reduction–oxidation behaviors of the cobalt crystallites, it could be seen that CO2 molecules acted as a mild oxidant by partially oxidizing the exposed metallic cobalt surfaces. The dramatic decrease in CO conversion and an increase in CH4 selectivity under the CO2 environment over CoAl were mainly attributed to the irreducible oxidation of the metallic cobalt surfaces through strong interactions with the Al2O3 support. Meanwhile, the marginal deactivation rate and lower changes of selectivity on CoSi were mainly attributed to the reversible oxidation–reduction property of the metallic cobalt crystallites by forming larger cobalt crystallites with relatively weak interactions with the SiO2 support. An excess exposure to the mild oxidant of CO2 on the FTS catalysts generally decreased the catalytic activity irreversibly by forming strongly interacted large cobalt crystallites, which was more predominantly seen on the acidic Co/Al2O3 than on the Co/SiO2 catalyst. The easy reversibility of the oxidation–reduction of the surface metallic cobalt crystallites on SiO2 even in the presence of excess CO2 could prevent catalyst deactivation during the FTS reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...