Atomic adsorption on graphene with a single vacancy: systematic DFT study through the periodic table of elements†
Abstract
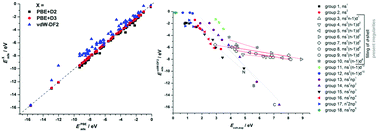
Vacancies in graphene present sites of altered chemical reactivity and open possibilities to tune graphene properties by defect engineering. The understanding of chemical reactivity of such defects is essential for successful implementation of carbon materials in advanced technologies. We report the results of a systematic DFT study of atomic adsorption on graphene with a single vacancy for the elements of rows 1–6 of the periodic table of elements (PTE), excluding lanthanides. The calculations have been performed using the PBE, long-range dispersion interaction-corrected PBE (PBE+D2 and PBE+D3) and non-local vdW-DF2 functionals. We find that most elements strongly bind to the vacancy, except for the elements of groups 11 and 12, and noble gases, for which the contribution of dispersion interaction to bonding is most significant. The strength of the interaction with the vacancy correlates with the cohesive energy of the elements in their stable phases: the higher the cohesive energy is, the stronger bonding to the vacancy can be expected. As most atoms can be trapped at the SV site we have calculated the potentials of dissolution and found that in most cases the metals adsorbed at the vacancy are more “noble” than they are in their corresponding stable phases.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...