A relationship between the force curve measured by atomic force microscopy in an ionic liquid and its density distribution on a substrate†
Abstract
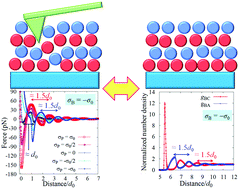
An ionic liquid forms a characteristic solvation structure on a substrate. For example, when the surface of the substrate is negatively or positively charged, cation and anion layers are alternately aligned on the surface. Such a solvation structure is closely related to slow diffusion, high electric capacity, and chemical reactions at the interface. To analyze the periodicity of the solvation structure, atomic force microscopy is often used. The measured force curve is generally oscillatory and its characteristic oscillation length corresponds not to the ionic diameter, but to the ion-pair diameter. However, the force curve is not the solvation structure. Hence, it is necessary to know the relationship between the force curve and the solvation structure. To find physical essence in the relationship, we have used statistical mechanics of a simple ionic liquid. We found that the basic relationship can be expressed by a simple equation and the reason why the oscillation length corresponds to the ion-pair diameter. Moreover, it is also found that Derjaguin approximation is applicable to the ionic liquid system.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...