Effects of non-equilibrium angle fluctuation on F1-ATPase kinetics induced by temperature increase†
Abstract
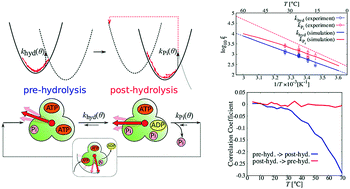
F1-ATPase (F1) is an efficient rotary protein motor, whose reactivity is modulated by the rotary angle to utilize thermal fluctuation. In order to elucidate how its kinetics are affected by the change in the fluctuation, we have extended the reaction–diffusion formalism [R. Watanabe et al., Biophys. J., 2013, 105, 2385] applicable to a wider range of temperatures based on experimental data analysis of F1 derived from thermophilic Bacillus under high ATP concentration conditions. Our simulation shows that the rotary angle distribution manifests a stronger non-equilibrium feature as the temperature increases, because ATP hydrolysis and Pi release are more accelerated compared with the timescale of rotary angle relaxation. This effect causes the rate coefficient obtained from dwell time fitting to deviate from the Arrhenius relation in Pi release, which has been assumed in the previous activation thermodynamic quantities estimation using linear Arrhenius fitting. Larger negative correlation is also found between hydrolysis and Pi release waiting time in a catalytic dwell with the increase in temperature. This loss of independence between the two successive reactions at the catalytic dwell sheds doubt on the conventional dwell time fitting to obtain rate coefficients with a double exponential function at temperatures higher than 65 °C, which is close to the physiological temperature of the thermophilic Bacillus.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...