Reaction mechanism of hydrogen evolution catalysed by Co and Fe complexes containing a tetra-dentate phosphine ligand – a DFT study†
Abstract
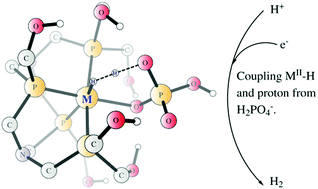
The reaction mechanism of the electro-catalytic proton reduction in neutral phosphate buffer enabled by mononuclear cobalt and iron complexes containing a tetra-dentate phosphine ligand (MP4N2, M = Fe, Co) has been elucidated by density functional calculations. The phosphate from the buffer was found to play a crucial role by coordinating to the metal and delivering a proton to the metal hydride in the H–H bond formation. For the more efficient cobalt catalyst, the starting species is a CoII complex with a hydrogen phosphate and a water molecule ligated at the two vacant coordination sites. Two sequential proton-coupled electron transfer reductions lead to the formation of a CoII–H intermediate with a dihydrogen phosphate ligand, and the reduction potentials for these two steps were calculated to be −0.58 V and −0.72 V, respectively. Subsequently, the H–H bond formation takes place via coupling of the CoII–H and the proton from the dihydrogen phosphate ligand. The total barrier was calculated to be 18.2 kcal mol−1 with an applied potential of −0.5 V, which can further decrease to only 11.2 kcal mol−1 with an applied potential of −0.8 V. When the phosphate is displaced by a water molecule, the total barrier for the dihydrogen formation increases by 7.3 kcal mol−1. For the iron catalyst, the overall mechanism is essentially the same; however, the first reduction (FeII/FeI, potential of −1.13 V) is likely the rate-limiting step. The calculated results are in good agreement with the experimental data, which showed an onset potential of −0.50 V for the cobalt complex and −1.03 V for the iron complex.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...