Effect of immobilization site on the orientation and activity of surface-tethered enzymes†
Abstract
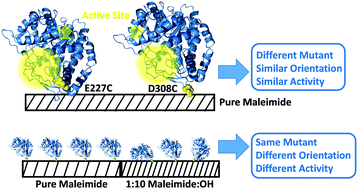
Tethering peptides and proteins to abiotic surfaces has the potential to create biomolecule-functionalized surfaces with useful properties. Commonly used methods of immobilization lack control over the orientation in which biological molecules are covalently or physically bound to the surface, leading to sub-optimal materials. Here we use an engineered beta-galactosidase that can be chemically immobilized on a surface with a well-defined orientation through unique surface-accessible cysteine residues. A combined study using sum frequency generation (SFG) vibrational spectroscopy and coarse grained molecular dynamics (MD) simulations was performed to determine the effects of enzyme immobilization site and abiotic surface chemistry on enzyme surface orientation, surface coverage, and catalytic activity. Two beta-galactosidase variants that were immobilized through cysteine introduced at positions 227 and 308 were studied. In both cases, when the abiotic surface was made more hydrophilic, the enzyme surface coverage decreased, but the activity increased. MD simulations indicated that this is due to the weakened interactions between the immobilized enzyme and the more hydrophilic surface. These studies provide improved understanding of how enzyme-surface interactions can be optimized to maximize the catalytic activity of surface tethered enzymes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...